 US Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen (center) arrives for the G20 finance ministers and central bankers meeting in Venice on July 9, 2021. (ANDREAS SOLARO / AFP)
US Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen (center) arrives for the G20 finance ministers and central bankers meeting in Venice on July 9, 2021. (ANDREAS SOLARO / AFP)
Finance ministers from the US and Europe expressed confidence that a global tax deal endorsed by the Group of 20 on Saturday has enough momentum to overcome domestic political obstacles in time for it to be finalized in October.
“There’s more work to be done, but I’m really hopeful that with the growing consensus we’re on a path to a tax regime that will be fair for all of our citizens,” US Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen told reporters on the sidelines of the G20 meeting in Venice.
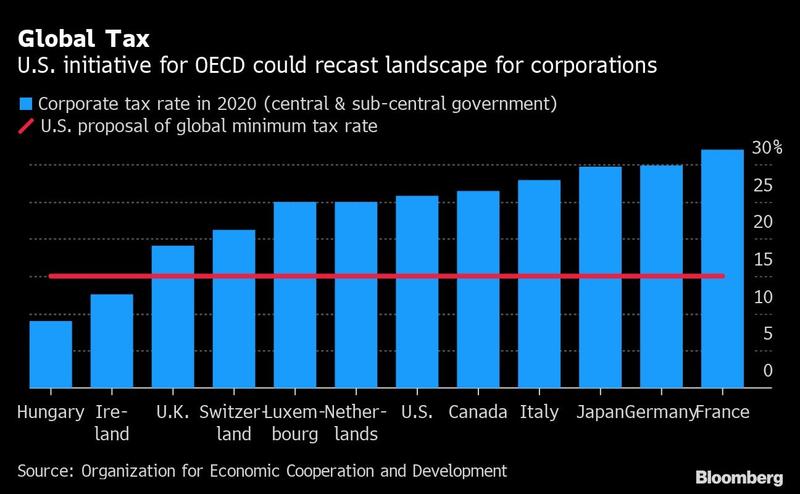
The landmark agreement aims to revamp rules that have allowed major companies to save billions by shifting profits to low tax jurisdictions
The landmark agreement aims to revamp rules that have allowed major companies to save billions by shifting profits to low tax jurisdictions. A total of 132 countries last week backed the two-pillar accord at the OECD that seeks to address that situation with a global minimum rate, as well as making multinational companies pay more in places where they operate rather than where they are headquartered.
ALSO READ: G20 to call for global tax deal to be finalized by October
Yellen was particularly confident that the US Congress would pass legislation needed to implement at least the part of the proposed deal that imposes a minimum tax rate.
“I’m very optimistic that the legislation will include what we need for the US to come into compliance with pillar 2,” Yellen said.
 German Finance Minister Olaf Scholz said he believes European holdouts Ireland, Hungary and Estonia would be brought on board. “This is a big historic moment. The G20 has now reached an agreement here for new rules on international taxation to be introduced,” he said.
German Finance Minister Olaf Scholz said he believes European holdouts Ireland, Hungary and Estonia would be brought on board. “This is a big historic moment. The G20 has now reached an agreement here for new rules on international taxation to be introduced,” he said.
France’s Finance Minister Bruno Le Maire said “there is no turning back” from the G20 officials giving their stamp of approval.
“It will be implemented and we will have built this international taxation system for the 21st century,” Le Maire said.
The three finance chiefs, whose countries have for years haggled over the details of an agreement, hailed the political endorsement in Venice as killing off a competition among countries that have sought to attract corporations with lower and lower taxes.
US Congress Hurdle
Getting that finalized, however, will require support from Congress, where many Republican lawmakers and some Democrats have expressed serious reservations about both so-called pillars of the deal.
Yellen said she has engaged in talks with the Democratic leaders of key congressional committees on the Biden administration’s tax proposals. These would cover not only the international agreement but also measures needed to pay for the president’s ambitious plans to invest in infrastructure and other priorities over the next decade.
The Treasury chief said changes necessary to comply with the minimum corporate taxes could be passed alongside other Biden proposals through a process known as budget reconciliation that won’t require Republican support in the closely divided legislature.
“Congress is negotiating a budget resolution that we expect to result in a reconciliation bill,” she said.
ALSO READ: Stung by pandemic, G20 foreign ministers urge more cooperation
Following Yellen’s remarks, a Treasury official said the administration sees approval for pillar 1, which proposes a redistribution of corporate tax rights on multinational firms, as moving forward on a different schedule.
That part of the deal won’t be approved until next year at the earliest, said the official, who commented on condition of anonymity because they weren’t authorized to speak publicly. The OECD accord foresees implementation in 2023.
Europe Hurdle
Scholz and other European leaders face their own internal fights to get the agreement adopted across the 27-member bloc.
Ireland, Hungary and Estonia have so far refused to sign up to the minimum tax, creating a potential roadblock because of the need for unanimity on tax issues within the EU.
While Scholz expressed optimism the three countries will eventually back the accord, the EU could yet create other problems because of a plan to present a digital levy for the bloc in the coming weeks. That has rankled Treasury officials, who point out that the OECD deal is supposed to eliminate taxes in several European countries on digital giants like Amazon.com Inc and Alphabet Inc’s Google.
The US has insisted such levies are abolished before a deal goes to Congress, and that no new ones be adopted. Yellen is due to meet with European counterparts in Brussels on Monday to discuss the matter.
READ MORE: WHO: Funding, vaccines sought from G20 nations for COVAX
“We can fix the issue, we can alleviate the difficulties,” Le Maire said. “There is and there are solutions and I’m sure that the European Commission will do its best efforts to find solutions with the American administration.”
Rate Hurdles
Besides possible implementation challenges, there are issues that remain to be settled between advanced and developing countries, and high and low tax jurisdictions.
On the minimum tax, Le Maire said he had agreed with Yellen and Scholz in Venice to push for a rate higher than 15 percent.
There also remain technical and political hurdles connected to sharing out of rights to tax international firms. According to the OECD deal, between 20 percent and 30 percent of profits over 10 percent of revenues would be allocated for tax in countries where multinationals generate revenues.
“For the time being we have consensus for 20 percent. I think that best solution would be a level of reallocation of 25 percent to meet the concerns of some developing countries,” Le Maire said.


