 In this file photo dated March 16, 2022, a man walks past the US Federal Reserve in Washington DC. (PHOTO / XINHUA)
In this file photo dated March 16, 2022, a man walks past the US Federal Reserve in Washington DC. (PHOTO / XINHUA)
BENGALURU - The US Federal Reserve will raise its benchmark overnight interest rate by 25 basis points to the 5.25-5.50 percent range on July 26, according to all 106 economists polled by Reuters, with a majority still saying that will be the last increase of the current tightening cycle.
A resilient economy and historically low unemployment well over a year since the Fed began one of its most aggressive rate hiking campaigns in history has repeatedly confounded analysts and investors.
Inflation is falling, with the headline consumer price index (CPI) measure slowing to 3.0 percent in June from 4.0 percent in May. That led many observers on Wall Street to conclude inflation might soon be tamed, prompting some to renew bets that rate cuts could happen by as soon as the end of 2023.
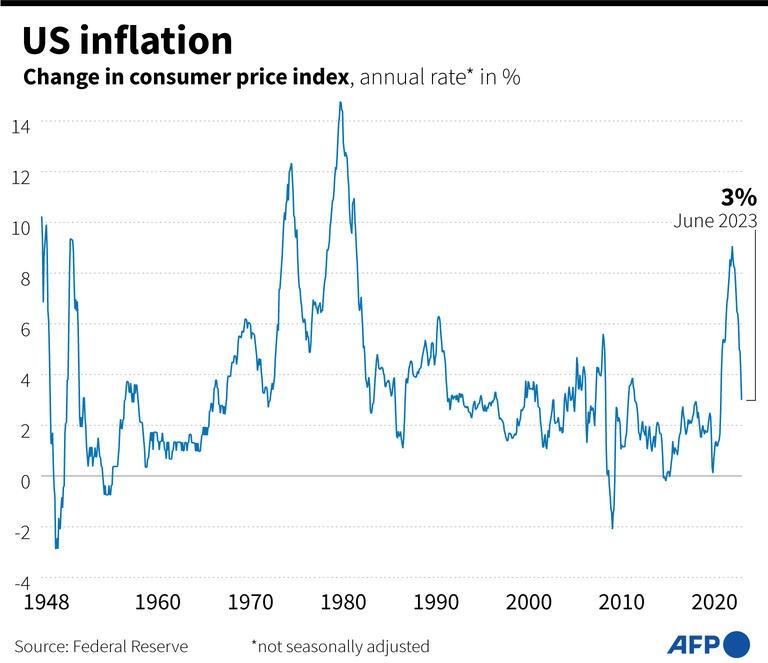 This AFP graphic dated July 13, 2023 shows the chart of changes in the US consumer price index since 1948.
This AFP graphic dated July 13, 2023 shows the chart of changes in the US consumer price index since 1948.
The current debate is whether more rate increases might be needed to ensure "disinflation" continues or if doing more could cause unnecessary damage to the economy.
Inflation is falling, with the headline consumer price index (CPI) measure slowing to 3.0 percent in June from 4.0 percent in May. That led many observers on Wall Street to conclude inflation might soon be tamed, prompting some to renew bets that rate cuts could happen by as soon as the end of 2023
But underlying inflation has remained sticky and Fed Chair Jerome Powell and other central bank officials have said more tightening is coming, even though they decided to pause the rate hikes at last month's policy meeting.
The view that rates will stay higher for longer appears to be gaining traction, with the share of respondents polled during the July 13-18 period who predicted at least one rate cut by the end of March next year down sharply to 55 percent from 78 percent last month.
ALSO READ: Fed leaves rates unchanged, sees two small hikes by end of 2023
"For the Fed, despite the soft CPI print, we still anticipate a hike in July ... (and) while we hope the softness in inflation persists, it is unwise from a policymaking standpoint to bank on that," said Jan Nevruzi, US rates strategist at NatWest Markets.
"We do not want to rush ahead and say the fight against inflation has been won, as we have seen head-fakes in the past."
Economists and financial market traders appear to still be slightly out of step with the Fed.
The latest "dot-plot" projections from members of the central bank's policy-setting Federal Open Market Committee suggest the benchmark overnight interest rate will peak at 5.50-5.75 percent, but only 19 of 106 economists polled by Reuters forecast it will reach that range.
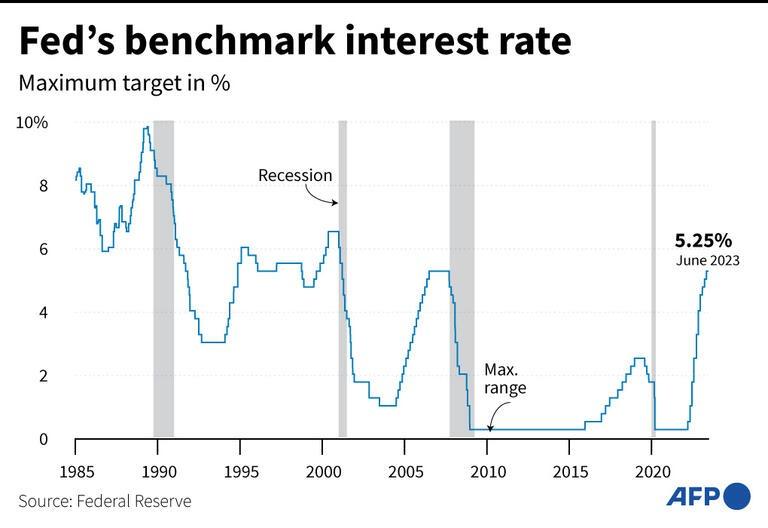 This AFP graphic dated June 15, 2023 shows the chart of changes in the benchmark interest rates of the United States Federal Reserve since 1985.
This AFP graphic dated June 15, 2023 shows the chart of changes in the benchmark interest rates of the United States Federal Reserve since 1985.
Expectations the Fed is nearing the end of its hiking cycle have pushed the dollar to its lowest level in more than a year against major currencies. A weaker greenback is likely to make imports costlier and keep price pressures elevated.
The latest "dot-plot" projections from members of the central bank's policy-setting Federal Open Market Committee suggest the benchmark overnight interest rate will peak at 5.50-5.75 percent, but only 19 of 106 economists polled by Reuters forecast it will reach that range
Indeed, economists are still concerned that inflation might not come down quickly enough.
Core inflation, which strips out food and energy prices, will be only slightly lower or remain around the current level of just under 5 percent by the end of the year, 20 of 29 respondents to an additional question in the poll said.
The Fed targets inflation, as measured by the personal consumption expenditures index (PCE), for its 2 percent target. Core PCE was last reported at 3.8 percent for May.
ALSO READ: Rents push up US consumer prices; inflation gradually cooling
But none of the inflation gauges polled by Reuters - CPI, core CPI, PCE and core PCE - were expected to reach 2 percent until 2025 at the earliest.
"While the latest figures are encouraging, the real battle begins now, as the easy base effects are now behind us," said Doug Porter, chief economist at BMO Capital Markets, referring to the fact inflation plunged so much in June partly because it was so elevated at the same time last year.
 A cart holds items in a grocery store on July 12, 2023 in Miami, Florida. (PHOTO / AFP)
A cart holds items in a grocery store on July 12, 2023 in Miami, Florida. (PHOTO / AFP)
"As the disinflationary force of lower energy prices fades, that will leave us dealing with the underlying 4 percent trend in core ... (and) to truly crack core will likely require a more significant slowing in the economy."
A slight majority of economists who answered an additional question, 14 of 23, said wage inflation would be the most sticky component of core inflation
The strong labor market is only expected to loosen slightly, nudging up the unemployment rate to 4.0 percent from the current 3.6 percent by the end of 2023, the poll showed.
A slight majority of economists who answered an additional question, 14 of 23, said wage inflation would be the most sticky component of core inflation.
Nearly two-thirds of respondents to a separate question, 27 of 41, expected a US recession within the next year, with 85 percent of them saying it would start at some point in 2023.
READ MORE: New Fed research flags rising risk of US recession
Still, the economy was expected to grow 1.5 percent this year, up from the 1.2 percent predicted a month ago, and then slow to 0.7 percent next year.


