 Yemenis, some wearing protective mask, shop at a street market in the Crater district of Yemen's southern coastal city of Aden on May 17, 2020, amid fears that coronavirus is spreading unhindered in the Yemeni city. (NABIL HASAN / AFP)
Yemenis, some wearing protective mask, shop at a street market in the Crater district of Yemen's southern coastal city of Aden on May 17, 2020, amid fears that coronavirus is spreading unhindered in the Yemeni city. (NABIL HASAN / AFP)
DUBAI / ADEN - Yemen, already pushed to the brink of famine by a five-year war, could see a “catastrophic” food security situation due to the coronavirus pandemic and lower remittances from the Gulf, the UN’s Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO) said on Monday.
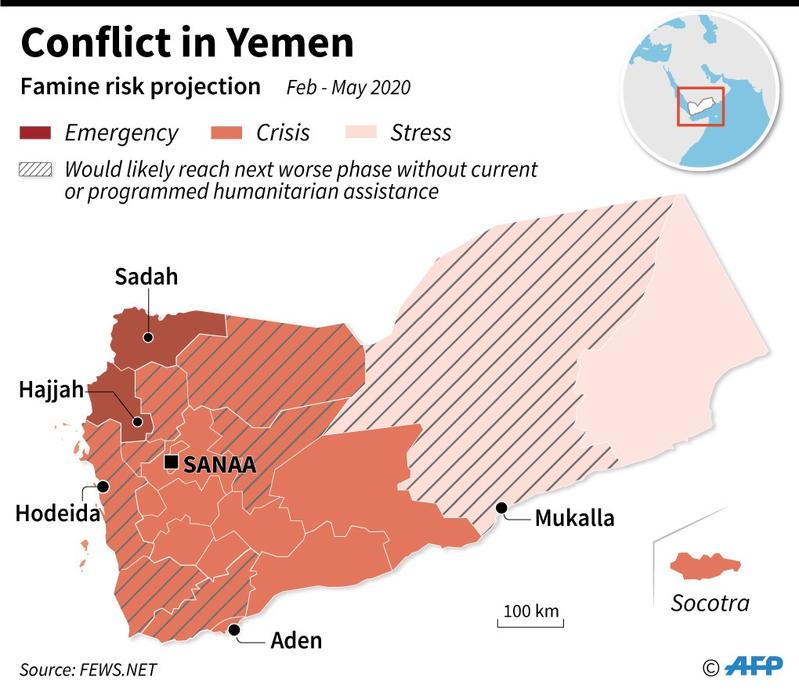
Some 80% of Yemen’s population are reliant on aid and millions face hunger
The conflict between a Saudi-led coalition and the Iran-aligned Houthi movement has caused what the United Nations describes as the world’s largest humanitarian crisis.
Some 80% of Yemen’s population are reliant on aid and millions face hunger.
“The health system was already under heavy stress and will now be overwhelmed if COVID-19 continues to spread and in addition it will affect the movement of people and the movement of goods,” Abdessalam Ould Ahmed, the FAO’s assistant director-general and regional representative for the Near East and North Africa, told Reuters.
Lockdowns to prevent the spread of the virus are likely to impact humanitarian supply chains keeping a large part of the population fed, the UN agency said in a report on Monda
“That situation could be really catastrophic if all the elements of worst case scenarios come to be but let’s hope not and the UN are working on avoiding that.”
Yemen, alongside Syria and Sudan, is one of the most vulnerable states in the Middle East in terms of food security.
READ MORE: Yemen reports first coronavirus case in Marib province
Lockdowns to prevent the spread of the virus are likely to impact humanitarian supply chains keeping a large part of the population fed, the UN agency said in a report on Monday.
Yemen has been mired in violence since the coalition intervened in 2015 against the Houthi group that ousted the Saudi-backed government in the capital, Sanaa, forcing it to rebase in the south.
The internationally recognized government has reported 128 COVID-19 infections with 20 deaths in areas under its control. The Houthis, who control most large urban centres, have announced four cases with one death, both in Sanaa.
ALSO READ: As virus cases in Yemen surge, some sources see undercounting
The Saudi-backed government accused the Houthis of covering up a big outbreak and called for urgent global assistance to help Yemen’s health sector deal with the coronavirus.
“Reports on the ground indicate a large number of coronavirus cases in areas under the Houthis’ control and hiding this information is completely unacceptable,” Yemeni Minister of Local Administration Abdul Raqib Fath told a news conference on Sunday.
The Houthi movement, which ousted the internationally recognized government from Sanaa in late 2014, denies the charges.
The Aden-based government also said Yemen urgently needed financial assistance and protective gear for health workers in addition to ventilators, polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and swab test equipment.
Circulating undetected
The World Health Organization said last Monday the virus was circulating undetected in Yemen, increasing the likelihood of a devastating outbreak among a malnourished population that would overwhelm a shattered health system with limited testing capacity.
The WHO says it has been advising local authorities throughout Yemen, where testing capacity is limited, to report cases in order to secure resources, but that the decision to do so rests with a country’s leaders.
Sources had told Reuters that both sides have not fully disclosed the extent of the pandemic in a country already plagued by other diseases.
There are currently 15.9 million Yemenis classified as food insecure out of a population of some 28 million.
The FAO does not currently have an estimate as to how much bigger that number could get if the disease continues to spread but it continues to monitor the situation.
The United States said on May 6 it would provide US$225 million to the World Food Programme (WFP) for Yemen, including for reduced operations in the north.
The WFP had said it would halve aid in Houthi-held areas from mid-April over donor concerns that the group is hindering aid deliveries, a charge it denies.
 This AFP map shows areas of territorial control in the Yemen conflict, as of February 13, 2020.
This AFP map shows areas of territorial control in the Yemen conflict, as of February 13, 2020.
The FAO said Yemen, the poorest Arabian Peninsula nation, would also be hit by an expected decline in remittances from Yemenis in Gulf countries, which amounted to US$3.8 billion in 2019.
“This is a significant source of income for the country that may be considerably reduced,” Ould Ahmed said.
Many foreign workers in the energy-producing region have lost jobs, been put on unpaid leave or had salaries cut due to the coronavirus and low oil prices.
“Without peace we will continue to struggle with food insecurity and there will be no long term recovery,” FAO said.
The UN envoy to Yemen said on Thursday that “significant progress” has been made toward cementing a temporary truce prompted by the coronavirus pandemic and to pave the way for a resumption of stalled peace talks.


