 The European Central Bank (ECB) building is pictured ahead of the meeting of the governing council of the ECB in Frankfurt am Main, western Germany, on July 27, 2023. (PHOTO / AFP)
The European Central Bank (ECB) building is pictured ahead of the meeting of the governing council of the ECB in Frankfurt am Main, western Germany, on July 27, 2023. (PHOTO / AFP)
FRANKFURT - The European Central Bank is set to decide on Thursday whether to raise its key interest rate to a record peak in what should be its final step in the fight against inflation, or take a break as the economy deteriorates.
The central bank for the 20 countries that share the euro faces a dilemma. Even after nine consecutive rate hikes, prices are rising at more than twice its 2 percent target and are not expected to slow to that level for another two years.
But higher borrowing costs across much of the world are taking a toll on economic growth, with a recession in the euro zone now a distinct possibility.
Analysts and investors had been leaning towards a pause in the ECB's rate increases until Reuters reported on Tuesday that the central bank was set to raise its forecast for inflation next year to more than 3 percent, bolstering the argument for a hike.
Policymakers saw the 2024 projection as crucial to determine whether inflation, currently still above 5 percent, was heading back to target or risked getting stuck at a higher level for too long.
Analysts and investors had been leaning towards a pause in the ECB's rate increases until Reuters reported on Tuesday that the central bank was set to raise its forecast for inflation next year to more than 3 percent, bolstering the argument for a hike
"The inflation momentum is simply too strong for the ECB to pause," Danske Bank economist Piet Haines Christiansen said.
A majority of economists in a Sept 5-7 Reuters poll had expected the ECB to hold rates steady this week but with the mood shifting, money markets now assign a 63 percent chance of a hike, expected to be the last in a cycle that began in July 2022.
ALSO READ: ECB raises rates to 23-year high; keeps options open for Sept
In contrast, markets have fully priced in unchanged rates at next week's meeting of the US Federal Reserve, which started raising rates earlier and has moved higher than the ECB.
An increase of 25 basis points on Thursday would take the rate the ECB pays on bank deposits to 4.0 percent, the highest level since the euro was launched in 1999.
Just 14 months ago, that rate was languishing at a record low of minus 0.5 percent, meaning banks had to pay to park their cash securely at the central bank.
UniCredit analysts said Thursday was a now-or-never moment for another rise in borrowing costs.
"If the ECB does not hike, it will sound hawkish and will try to convince financial markets that rates could be moved higher at one of its subsequent meetings," they said in a note.
"We doubt that this will be possible and expect that a decision to hold rates steady today would mark the end of the tightening cycle."
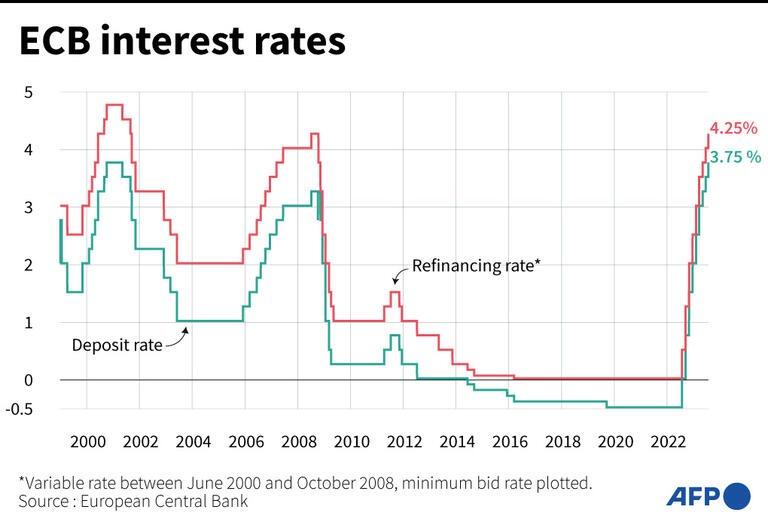 This AFP graphic dated July 27, 2023 shows the chart of changes in interest rates set by the European Central Bank (ECB) from 1999 to July 2023.
This AFP graphic dated July 27, 2023 shows the chart of changes in interest rates set by the European Central Bank (ECB) from 1999 to July 2023.
New forecasts
Supporters of a hike this week are likely to argue it is needed because inflation, including underlying measures that strip out volatile components, remains too high, with a recent surge in energy prices threatening a new acceleration.
But the brisk tightening cycle - twice as steep as normally envisaged by the ECB's own stress tests of the banking sector - has already left its mark on the euro zone economy.
With the manufacturing sector, which typically needs more capital to operate, already suffering as a result of higher borrowing costs, lending to companies and households has fallen off a cliff.
Supporters of a hike this week are likely to argue it is needed because inflation, including underlying measures that strip out volatile components, remains too high, with a recent surge in energy prices threatening a new acceleration
Services has now also started to struggle following a brief post-pandemic boom in tourism.
The euro zone's biggest economy, Germany, is bearing the brunt of an industrial slump and heading for recession, according to several forecasts.
READ MORE: ECB meets over banking stress as US rescue eases immediate fears
On Thursday, the ECB is also expected to cuts its growth projections for this year and next, leading some economists to argue it should hold off from raising rates this month.
"While core inflation is only showing tentative signs of easing, the growth outlook has darkened quickly, implying less need for tightening," Natixis economist Dirk Schumacher said.
Once its rate increases end, the ECB is likely to begin a debate on mopping up more of the cash it pumped into the banking system through various stimulus schemes over the last decade, although no decision on that matter was expected this week.


