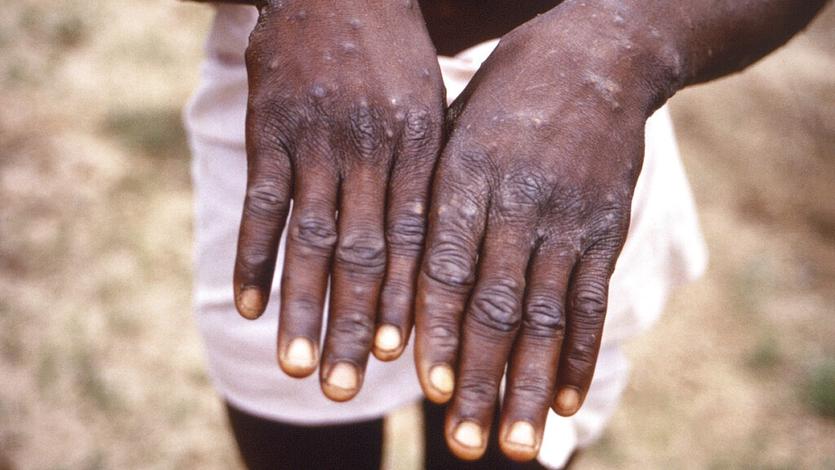
 This 1997 image provided by the CDC during an investigation into an outbreak of monkeypox, which took place in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, depicts the dorsal surfaces of the hands of a monkeypox case patient, who was displaying the appearance of the characteristic rash during its recuperative stage.
(CDC VIA AP)
This 1997 image provided by the CDC during an investigation into an outbreak of monkeypox, which took place in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, depicts the dorsal surfaces of the hands of a monkeypox case patient, who was displaying the appearance of the characteristic rash during its recuperative stage.
(CDC VIA AP)
LONDON - The World Health Organization does not believe the monkeypox outbreak outside Africa will lead to a pandemic, an official said on Monday, adding it remains unclear if infected people who are not displaying symptoms can transmit the disease.
More than 300 suspected and confirmed cases of monkeypox - a usually mild illness that spreads through close contact and can cause flu-like symptoms and pus-filled skin lesions - have been reported in May, mostly in Europe
More than 300 suspected and confirmed cases of monkeypox - a usually mild illness that spreads through close contact and can cause flu-like symptoms and pus-filled skin lesions - have been reported in May, mostly in Europe.
ALSO READ: China tightens curbs to prevent import of monkeypox virus
The WHO is considering whether the outbreak should be assessed as a "potential public health emergency of international concern" or PHEIC. Such a declaration, as was done for COVID-19 and Ebola, would help accelerate research and funding to contain the disease.
Asked whether this monkeypox outbreak has the potential to grow into a pandemic, Rosamund Lewis, technical lead for monkeypox from the WHO Health Emergencies Program said: "We don't know but we don't think so."
"At the moment, we are not concerned of a global pandemic," she said.
ALSO READ: WHO: Monkeypox presents moderate risk to public health
Once monkeypox has been contracted, the duration of the rash emerging and scabs falling off is recognized as the infectious period, but there is limited information on whether there is any spread of the virus by people who are not symptomatic, she added.
"We really don't actually yet know whether there's asymptomatic transmission of monkeypox - the indications in the past have been that this is not a major feature - but this remains to be determined, she said.
The strain of virus implicated in the outbreak is understood to kill a small fraction of those infected, but no deaths have been reported so far.
ALSO READ: WHO expects more cases of monkeypox to emerge globally
Most cases have cropped up in Europe rather than in the Central and West African countries where the virus is endemic, and are predominantly not linked to travel.
Scientists are therefore looking into what might explain this unusual surge of cases, while public health authorities suspect there is some degree of community transmission.


